E-mobility plays a crucial role in ensuring the greater sustainability of day-to-day life. However, it currently takes longer to charge an electric vehicle at a conventional charging station than it does to refuel a car with a combustion engine. The charging time also varies depending on the charging station. In smaller towns connected to the local power grid, the available grid capacity is often not sufficient to allow charging in minutes. This is because the grids tend to be low-voltage. By contrast, the medium- and high-voltage grids that are often found in industrial areas or close to highways can be used to operate high-power charging stations that allow rapid charging in high output ranges.
E-Mobility: About charging stations and charging time
According to Statista, there was a total of 120,625 public charging stations in Germany in 2024. In terms of network infrastructure, Germany therefore ranks second in Europe, followed by France with 119,255 charging stations and the United Kingdom with 72,924. The Netherlands currently leads the way in Europe with 144,453 charging stations.
The charging time not only depends on the output of the charging station, but also on environmental factors such as temperature, the technical configuration and the electric vehicle’s battery capacity. The higher the battery capacity, the higher the charging capacity and, of course, the range of the vehicle after charging. In practice, however, the onboard electronics of most electric vehicles automatically reduce the charging speed during high power charging once the battery level goes above 80 percent in order to protect key power electronics components.
Sources: Bundesnetzagentur, www.enercity.de, www.statista.com

Efficient cooling for demanding electromobility
ebm-papst offers cooling solutions for all systems related to electric vehicle charging.
As e-mobility becomes increasingly popular, there is a general need to upgrade the local electricity grid so that high power charging can be provided in rural areas as well, supporting the energy infrastructure by way of decentralization. On the one hand, this expansion is the task of grid operators. On the other hand, increasing the line voltage is not enough in itself to charge electric vehicles as quickly as possible.
For one thing, the vehicle electronics must also be compatible with the higher voltage, which is not yet the case for every model. However, there is now a solution that already works with the existing grid and the limited capacities provided by low voltages and the current status of electric vehicle electronics: charging stations with integrated battery storage systems.
Double charging thanks to battery storage systems
Charging stations with integrated battery storage systems are connected to the low-voltage grid. The batteries are charged continuously at the existing line voltage and available grid capacity and store this electrical energy. When the charging process starts, the charging station automatically combines the available grid output with the power stored in the battery storage system. Assuming the charging station has a maximum output of around 300 kilowatts, it takes just a few minutes to charge a standard electric vehicle sufficiently to travel more than 100 kilometers.
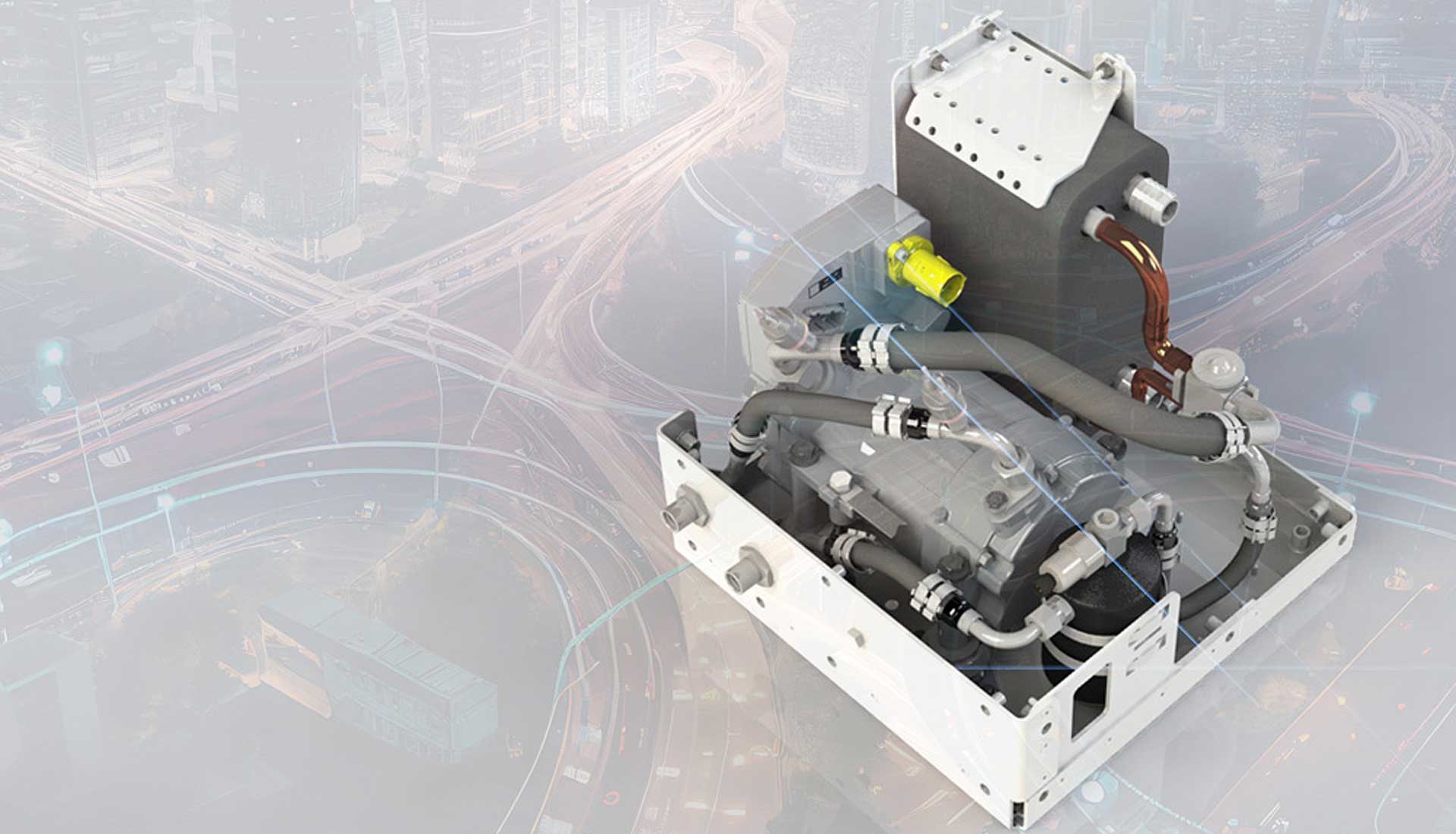
(Image | technotrans)
By comparison, conventional charging stations have an output of between 50 and 100 kilowatts. Although the output of high power charging stations is between 100 and 350 kilowatts, they can only be used with medium- to high-voltage grids. This is the advantage of charging stations with integrated battery storage systems.
While the car is still charging, the batteries are also being recharged (depending on the grid capacity) and will soon be ready for the next vehicle. It is important that the charging station batteries do not overheat during the many charging and discharging processes because this may slow the charging process and overload the components and the electric vehicle itself. This is exactly the right task for technotrans and its experts for the energy management and cooling of power electronics.
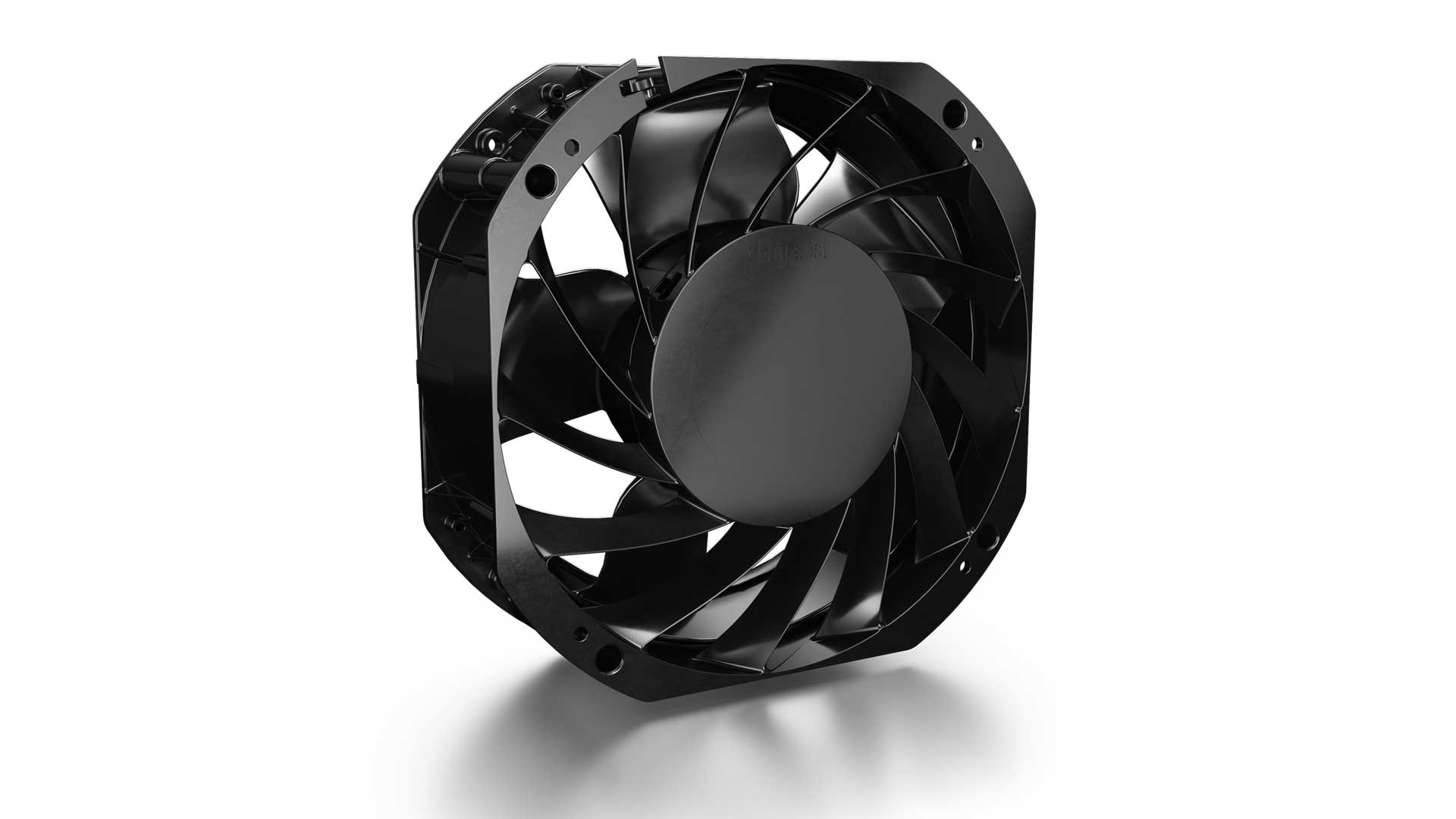

Air cooling is the ideal solution
technotrans is developing a cooling system for charging stations with battery storage systems. Air cooling is an ideal solution for these charging stations. The technotrans system uses a closed air circuit to cool the individual battery cells in the storage system. To this end, four AxiEco 200 compact fans are installed in the cooling system to circulate the natural ambient air. In this way, technotrans ensures that the batteries and power electronics for internal charging and simultaneous vehicle charging are cooled, thereby maintaining the high charging capacity.
Cooling takes place via an active refrigeration circuit, which keeps the air temperature for the batteries constant even in extreme ambient conditions. One aspect is particularly crucial to cooling the battery cells efficiently: a high air flow in the most compact space possible. For technotrans, the 500-watt motor and size of just 200 millimeters were the key factors in favor of the AxiEco 200: a lot of power in a small space.
Perfectly adapted
In addition to the power density, the demand-based operation of EC fans is also crucial. Most charging stations with battery storage systems are located in public places such as supermarkets or parking lots and only operate at full output when this is necessary. The charging stations and their batteries are exposed to fluctuating outdoor temperatures and adverse ambient conditions, which may affect the charging process and the durability of the components. However, this is not a problem thanks to the custom-manufactured plug connector used in the AxiEco 200.
“The AxiEco 200 enables the electronic system to selectively control the fan speed, thus adjusting the temperature in the battery cells for cooling as required.”
Bernhard Thürmer, Sales Engineer at ebm-papst
Bernhard Thürmer, sales engineer at ebm-papst, says: “In addition to the standard operating connection, the connector is also fitted with a speed control input and a speed output signal. This enables the electronic system to selectively control the fan speed, thus adjusting the temperature in the battery cells for cooling as required.” Thanks to these individual settings, the batteries are kept at the perfect temperature and their output is maintained, both on hot summer days and when it is icy cold.

Leave a comment