When existing drives need to be replaced, the available attachment points often need to be taken into account. Drop-in replacement, i. e., simply exchanging motors when the relevant parts have identical dimensions, is then called for. It is quite all right for the shapes and dimensions of the motors to vary, but shaft diameter and length, vibration absorbers and hole diameters on mounting brackets should be identical. Since (built-in) household appliances are usually manufactured with standard dimensions, smaller drives mean more usable volume. They also facilitate the integration of parts for new convenience functions.
In addition to these mechanical considerations, an increasing number of legal requirements now needs to be met. In both the EU and the US, in Canada and other countries, there is a host of laws, guidelines, directives and energy conservation standards imposing application-dependent minimum requirements on the energy efficiency of appliances.
ebm-papst uses flexible, electronically commutated DC motors even at low output levels.
In the EU, the Ecodesign Directive 2009/125/EC provides the necessary framework for specifying requirements for the environmentally compatible design of energy-related products (ErP), including the transparent presentation of the energy efficiency classes A+++ to G on energy labels affixed to appliances. Depending on the application, even small savings can be important in enabling a manufacturer to advertise higher efficiency with a better label.
And what does this mean in practice?
Simple motor designs such as shaded-pole or asynchronous motors are often no longer able to fulfill modern energy consumption and power density requirements. Motor and fan manufacturers such as ebm-papst Landshut therefore use flexible, electronically commutated DC motors even at low output levels. In contrast to conventional asynchronous shaded-pole motors, these small synchronous motors are highly efficient.

Figure 1: Aerodynamically optimized: VHD 0146 standard blower with standardized outlet and contact protection integrated in the intake.
In some cases, the commutation electronics even take over the functionality of a wide-range voltage input; such motors can be used without modification in almost all of the world’s power networks, making adaptations due to differences in grid frequency (50 or 60 Hz) unnecessary. Thanks to their ingenious designs, these compact motors can be integrated into a number of applications.
Three example drive applications demonstrate the potential of EC motors: a compact motor for a dual-intake range hood blower; a drive for refrigerated display cases, refrigerators, freezers and refrigerator-freezers; and a centrifugal fan for drying applications.
Centrifugal fans for extraction systems
When large volumes of air need to be moved at medium to high pressure increases, dual-intake centrifugal fans are ideal. They are used in both household and technical applications, such as range hoods or soldering fume extractors.
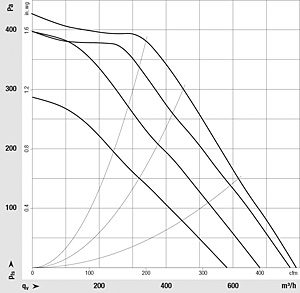
Figure 2: The VHD 0146 EC blower for range hoods covers typical air performance requirements in the range from 600 to 800 m³/h (free jet), replacing up to three AC blowers.
In addition to improved energy efficiency, operating noise needs to be kept as low as possible. Range hood blowers such as the VHD 0146 are supplied as complete units comprising motor, impeller, and fan housing with corresponding aerodynamic optimization of the intake/outlet (Fig. 1 and 2).
With their compact form, EC motors leave more space for the aerodynamic design. In addition, their speed and air performance can be easily controlled with the commutation electronics, for example by pulse width modulation. Depending on the motor model and fan series, additional features such as moisture or temperature sensors can be integrated for an automatic ventilation system.
Refrigeration applications
The air flow inside modern refrigerators and outside at the condenser is optimized by fans, which can be used to break up temperature stratification or, with directed circulation of cold air, to create fresh food zones or prevent condensation. Air flow routed through the condenser improves heat transfer; heat sinks can be more compact, increasing both the efficiency and the capacity of refrigerators.

Figure 3: The DE 20 motor is specially optimized for refrigerators and freezers and is designed for standard speeds of 2,200 or 2,500 rpm in combination with a four-blade impeller with a diameter of 100 mm.
To make use of the efficiency of EC motors in existing appliances, the specialists in Landshut have developed the DE 20 motor specially for refrigerators and freezers. The motor’s shaft length and diameter are the same as those of the shaded-pole motors previously used, so the spacing between the impeller and the heat exchanger (evaporator or condenser) can be maintained. The motor and the electronics are enclosed in a smooth housing, and the unit is connected as before with a two-wire cable. With a height of 40 mm, the housing dimensions correspond to the most commonly used standard size (Fig. 3).
With electronic commutation, the motor speed is decoupled from the line frequency, so the fan’s size and shape can be chosen according to purely aerodynamic considerations and its speed is adjustable. Fans with standard speeds of 2,200 or 2,500 rpm and a four-blade impeller with a diameter of 100 mm fit in many refrigerators as drop-in replacements. In this way, energy consumption can be reduced easily when modernizing product lines.
Time-saving and efficient laundry drying
Centrifugal fans are ideal when high air performance and a significant pressure increase are needed. They are used in applications such as clothes dryers and washer-dryers. Heat pump systems are often used in such appliances for efficiency reasons. They heat the air for drying the laundry in the drum. In a cycle, the heat pump extracts the heat and condenses the water from the warm, moist “exhaust air” and uses the recycled energy to reheat the now cold and dry “intake air.”
Only minimal heat losses need to be compensated, which reduces power consumption. However, additional components such as compressors, condensers and evaporators used in heat pumps need space. And the capacity of laundry drums has risen over the years from about 5 kg to as much as 15 kg. Both factors limit the space available for additional components since the standard outer dimensions of household appliances stay the same.
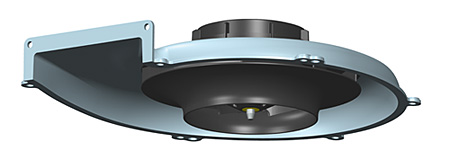
Figure 4: With its compact design, the R3G 150 centrifugal fan with EC drive delivers high air performance even where space is limited.
A new, very compact centrifugal fan is the answer to this trend. With its compact design, the R3G 150 centrifugal fan with EC drive (Fig. 4) can deliver high air performance even where space is limited. Compared with previous AC solutions, it offers better performance in terms of both pressure increase and air flow. Higher air flow at higher pressure allows a more compact fan design. The higher motor speed enabled by the use of EC technology allows the use of a smaller, aerodynamically modified impeller. The miniaturized fan that results can fit in the smallest corner.
Increasing demands on motor energy efficiency and the trend toward ever smaller size at ever greater output are being met by developers with customized EC motors. Compact size, speeds independent of the line frequency, and exchangeable plug & play designs make the new drives the ideal choice for savings. Depending on application, operating mode and model, potential energy savings can be as high as 70%. This enables appliance manufacturers to quickly and easily modernize existing household appliance product lines, in the best case simply with drop-in replacement.

Leave a comment