WHAT THE TECH?! How maintain fans according to demand?
What does Predictive Maintenance mean? And how can it improve my system?
Find the answer here: simple, understandable and with a bit of humor!
In addition to the lowest possible energy consumption, reliability is the key consideration when it comes to supermarket cooling. If a fan fails, it is important to locate and rectify the fault quickly to prevent the cold chain being interrupted and, in the worst case scenario, the food being spoiled.
Fans with intelligent energy-saving motors with GreenTech EC technology provide important information about the MODBUS RTU serial communications interface. In this way, intelligent maintenance concepts based on the actual maintenance requirements can be implemented correctly. And, thanks to their high efficiency levels, the energy-saving fans make a significant contribution to reducing operating costs.
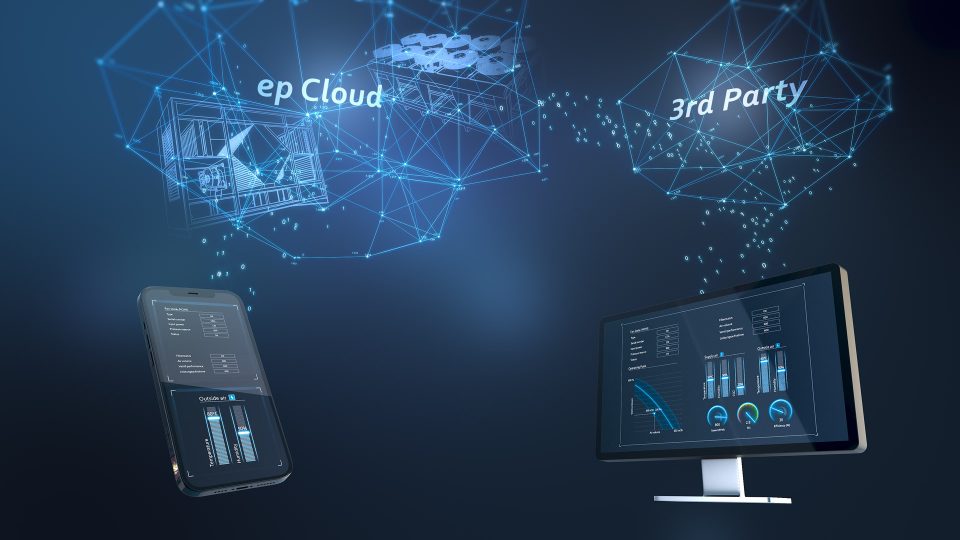
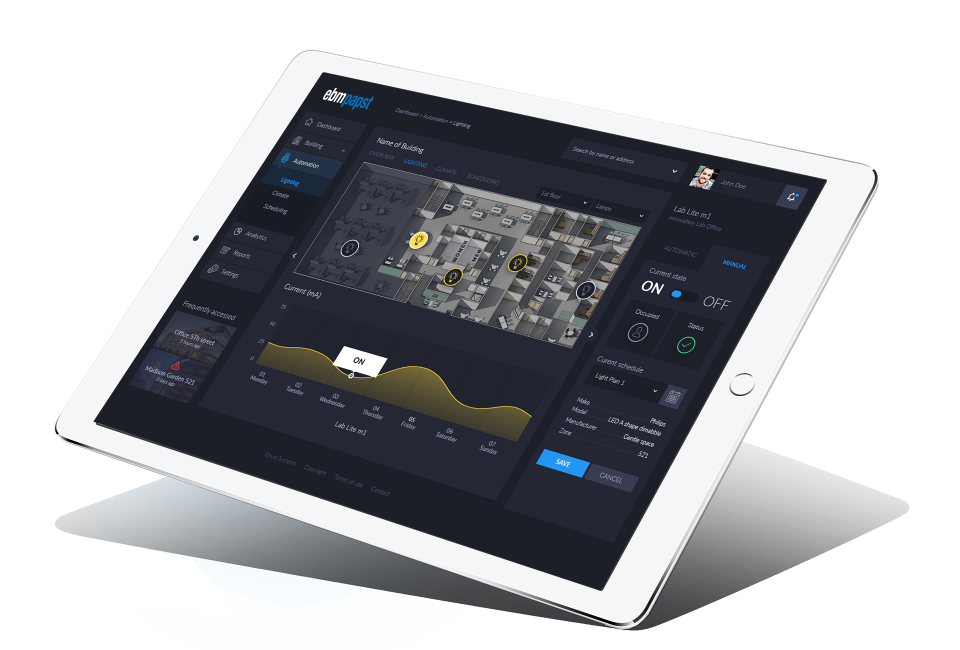
Continuous monitoring of all cooling operation components in supermarkets (Fig. 1) forms the basis for predictive maintenance, i.e. detecting faults before failure occurs and, in the worst case, the cold chain is interrupted. Facility managers and maintenance companies benefit from this equally, as it means that staff-intensive, regular maintenance is no longer necessary, or at least rarely. This reduces costs and is a decisive advantage even if there is a shortage of skilled workers.

It is essential that the higher-level control system communicates with the components used in refrigeration and freezer units and the central air conditioning. For example, anomalies in the normal operating behavior can be identified at an early stage using fan data, and targeted countermeasures can be introduced. To do this, the data supplied by the fan drives via MODBUS RTU must be evaluated and interpreted in real time as far as possible, taking into account the specific fan properties and the specific operating conditions.
With the Computation Cloud (Fig. 2) from ebm-papst neo, motor and fan specialist ebm-papst now offers a practical solution that is not only suitable for monitoring its own fans but also for other components used in the application, such as sensors, lighting units or similar. The specialists are happy to advise here and adapt the options to the individual supermarket control system.

Continuously monitoring fan operation
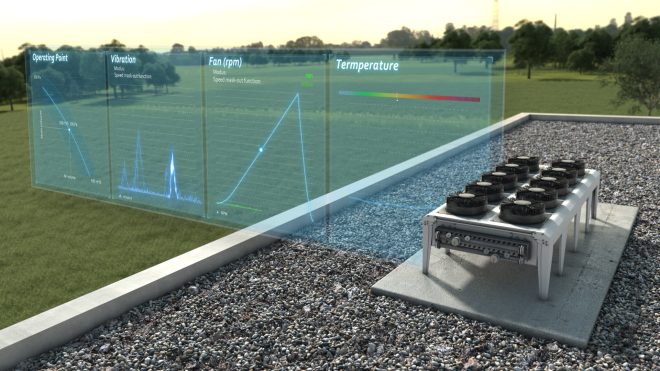
The latest fan generations from ebm-papst can transfer up to 200 data points to the higher-level control system, which can then be evaluated in the Computation Cloud. This provides meaningful information about every single fan (Fig. 3) in real time, from compact fans in refrigerated cabinets to large fans in the chiller on the roof of the supermarket.
Based on the data transmitted about the actual operating conditions, this can be used to calculate the expected remaining service life, for example. The key characteristic values here include the ambient temperature, shifts at the operating point, air flow, speed and vibrations that indicate abnormal loads. If the outage date approaches, the maintenance staff can order the appropriate replacement in good time using the part number, which is then replaced one-for-one before the expected failure occurs. The right replacement unit is then at your fingertips.
The cloud analysis also makes it possible to plan a wide range of maintenance measures, for example if the rotor blades of the axial fans used here begin to freeze on the chiller (Fig. 4), which can be expected in particular in winter when the temperatures outside are low. Before the resulting imbalance leads to bearing damage, service staff can check the fans and remove the ice formation. In turn, air flow, speed and current draw allow conclusions to be drawn as to whether and when filters need to be cleaned or replaced. When planning maintenance for chillers, the cooling water quantity can also be included in the calculations.
Efficiency in focus
The targeted deployment of maintenance staff saves the service team’s time and the operator’s money. The latter also benefits from avoiding outages in advance and the cold chain is not at risk. In addition, the intelligent EC fans are energy-efficient, which noticeably reduces electricity costs.
For example, EC motors from the ESM series (Fig. 5), which are typically used in refrigerated display cases, operate at efficiency levels of over 70% at just 10% of the power consumption of comparable shaded-pole motors. The speed control system enables demand-based operation. The display case is cooled accordingly depending on how often the display case is opened.
The compact EC motors are available as a complete plug-and-play system in which the individual components are perfectly coordinated with one another. Examples include the energy-saving fans W1G 250 and K1G 250. The W1G axial product range is intended for installation beneath the shelves of refrigerated and freezer cabinets. By contrast, the K1G product range with diagonal fan impeller was specially designed for the rear wall of refrigerated display cases, where there is often limited installation space. Thanks to their extremely shallow design, these fans fit in confined spaces and the diagonal fan design makes them well equipped to deal with the higher back pressure found in these spaces.

The high-performance EC motors in the large axial fans for chillers work at efficiency levels of over 90%. The aerodynamic optimization of the fan blades also makes the EC fans extremely quiet. This ensures that noise protection regulations are easily fulfilled, avoiding trouble with the neighbors. The efficiency levels can be checked at any time using the computation cloud by calling up the operating points and analyzing them in real time.
Discover more:
Datadriven buildings
Solutions for improved air quality and more


Leave a comment